TL;DR: Learn about the importance of remote network monitoring tools and how they can optimize network performance. Explore best practices for implementing remote network monitoring solutions.
Introduction to Remote Network Monitoring Tools
Remote network monitoring is an important aspect of network management that concerns distributed network infrastructures. This purpose-built network monitoring system detects remote network problems, facilitating quick response to outages and network performance issues at any remote location. Thanks to this management tool, network administrators gain actionable insights without being physically present at the network’s location. For this reason, remote network monitoring is essential for businesses that rely on robust and reliable network operations across multiple locations. Organizations in need for better monitoring and control across multiple locations, will greatly benefit from this network observability tool.

Understanding the Significance of Remote Network Monitoring
Challenges Addressed
Large network infrastructures with several distributed remote locations pose considerable challenges to network administrators. Traditional network monitoring solutions based on the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) provide mostly network devices status and performance. The network data reported by these systems delivers minimal insights into the experience of remote users as it’s mostly focused on network device monitoring. For instance, when users report a suspected problem with the network, or the application, the help desk team has little information to start troubleshooting. As a result, finding the root-cause of these problems takes a considerable amount of time and resources, and may require escalation to the higher support levels. Ultimately, lack of proper remote network monitoring increases the cost of network downtime and the support burden.
Benefits
Remote network monitoring has several benefits. First of all, a remote network monitoring system allows network administrators to gather the status and performance of remote networks in real time, including the end-user experience. Where traditional network monitoring tools provide network traffic statistics of Local Area Networks (LAN), remote network monitoring delivers more actionable insights. For instance, the help desk can verify real-time and historical data about end-to-end performance to SaaS and web applications. A remote network monitoring tool can include information such as available internet speed and wireless signal strength. This method of network monitoring is particularly suited for highly distributed network infrastructures. Remote network monitoring software and hardware helps detect potential network issues, and ensure optimal functioning without being physically present at all network location. This performance management solution enables the achievement of optimal performance of a network infrastructure as it ensures continuous network testing to key applications.
Remote Monitoring and Management
Remote network monitoring software is also an indispensable solution for Managed Service Providers (MSP). MSPs are businesses that provide remote network monitoring management, help desk, and support functions to organizations that prefer to outsource this critical function. Generally, remote network management tools used by MSPs also support multi-tenancy. Multi-tenancy allows MSPs to create and manage remote networks that belong to different organizations (clients’ networks) from the same system. These specialized tools are also called RMM, which stands for Remote Monitoring Management. Not all remote network monitoring tools are necessarily considered RMMs mostly due to a lack of multi-tenancy capabilities.
Remote Worker Network Monitoring
An important use case for remote network monitoring relates to monitoring the end-user experience of work from home users. Residential environments pose considerable challenges to network administrators, who have provide tech support and help desk services to remote employees. Differently from an enterprise network, work from home environments rely on a network infrastructure that is public, and not managed by the central IT department. As a result, troubleshooting work from home issues could be a very complex and time consuming task. Remote network monitoring enables IT to regain the network visibility lost, and reduce troubleshooting time. This is possible by software clients that run on the end-users desktops and laptop systems to perform the required data collection and diagnostic for troubleshooting.

Highlight: Read more about the State of Remote Work 2024 report to learn more about the top challenges faced by network operations teams when support remote users.
Key Components of Remote Network Monitoring
The monitoring probes
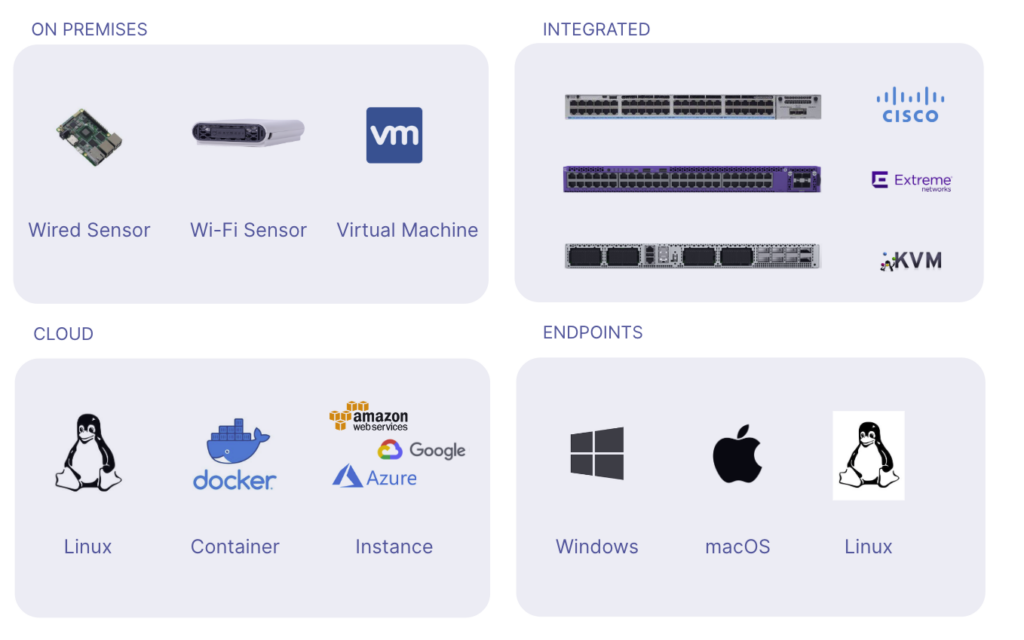
Remote network monitoring is accomplished by deploying a mix of software and hardware agents that are installed at remote networks. The agents, also called network probes, run continuous network tests against web and SaaS applications, collecting network performance metrics, end-user experience insights, and various diagnostic data. For instance, a remote network monitoring tool like NetBeez supports a variety of deployment options for monitoring probes, such as:
- Hardware-based appliances for small remote sites,
- Virtual images, software packages, and containers for data centers or locations with a hosting infrastructure, and
- Software clients for end-user systems based on Windows, Mac OS, and Linux.
The central server
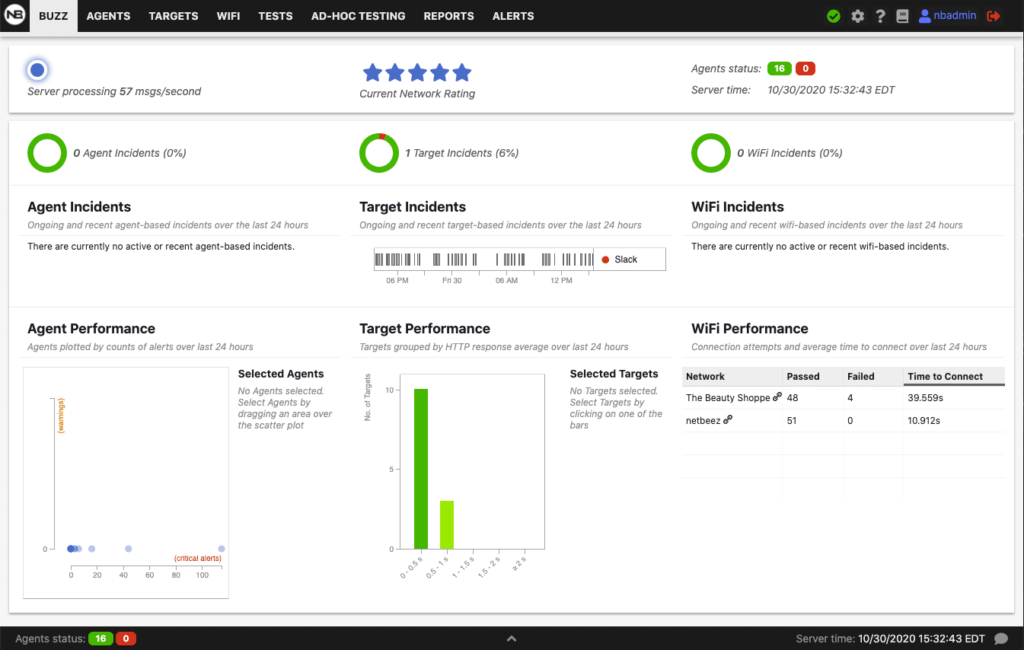
The central server processes in real time the network performance and diagnostic data collected by the agents. This key component is responsible for analyzing, displaying, and storing the information received. By doing so, the server can alert the network operations team about potential issues. As a result, the engineering team can perform proactive maintenance work on the infrastructure, and proactively troubleshooting emerging network problems. Associated with the central server is a user dashboard that allows network administrators and support staff to:
- Visualize the status of all remote network locations and users,
- Troubleshoot any ongoing network issues, and
- Interact with the remote network monitoring probes.
Choosing the Right Solution
Choosing the right remote network monitoring solution is a critical decision for any organization, but it can be complex and time-consuming. Several key factors must be considered to ensure the tool meets your specific needs. Not surprisingly, identifying the right tool was highlighted as one of the top 8 key challenges for IT Operations in 2024.
First of all, it’s important to list all the key requirements the solution should match, starting from the most important to the least important. Then, during the research and evaluation phase, apply scores to each requirement. This method will help save time in the process.
Over the past few years, we’ve partnered with numerous companies as they implemented remote network monitoring solutions. Based on these experiences, we’ve identified key success factors that consistently contribute to a solution’s effectiveness.
Network performance metrics collected
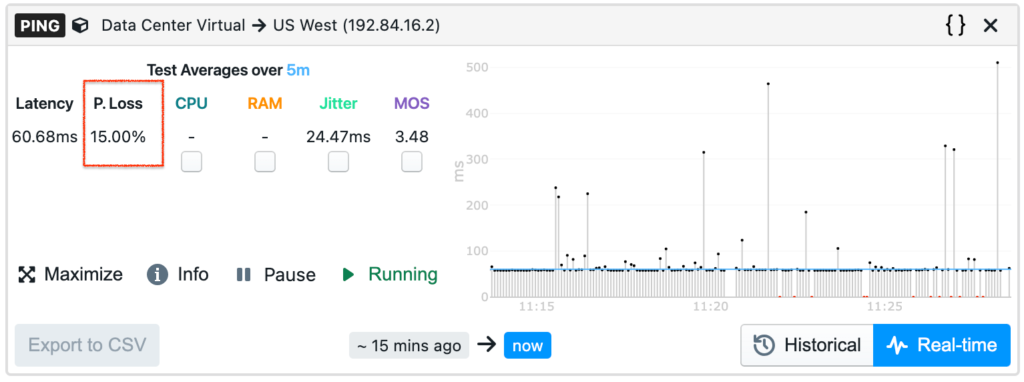
The solution should be able to collect in real time a variety of metrics that are necessary to proactively detect and diagnose remote network issues, such as packet loss, latency, network speed, and more.
Customizable network monitoring alerts
The solution should give the ability to define the metrics and alert triggering criteria that deliver proactive notifications. Alerting rules should support basic up-down events, as well as changing performance over time and against set thresholds.
Scalability
The solution should be able to accommodate the growth of the entire network under observation without requiring frequent server upgrades.
Compatibility and interoperability
The solution should be able to easily integrate with the underlying network infrastructure and network management system without the need for custom development.
Usability and reporting capabilities
A solution that is intuitive, easy to use, and requires minimal training is always preferred, as it reduces time to onboard new network administrators and operators.
Best Practices for Implementing Remote Network Monitoring
Implementing remote network monitoring requires adherence to best practices to ensure that the installation achieves the desired results. First of all, it’s important to start with an assessment of the number of remote locations. Organizations that embraced remote or hybrid work, should also include in the scope the number of work from home users. This initial assessment will guide the number of types of network monitoring agents that should be deployed. Second, the implementation will cover integrating the tool with the existing set of network management tools and network devices employed by the organization. This review will ensure that the remote network monitoring solution is successfully integrated within the IT operations of the organization. Lastly, the implementation should focus on training the IT staff on how to use the tools and establish clear protocols for responding to alerts.
NetBeez a Tool for Hybrid Networks
NetBeez is a remote network monitoring tool that provides a truly distributed and easy to use solution for today’s organizations. The solution was developed to address the challenges that network administrators face everyday ensuring optimal digital experience in highly distributed network infrastructures. It offers a comprehensive set of network performance metrics and end-user experience insights, enabling IT staff to cut troubleshooting time and saving resources when supporting remote locations and users.
NetBeez tackles three main use cases:
- Hybrid cloud monitoring: from WAN locations to public and private clouds, NetBeez offers flexible deployment options for measuring end-to-end network performance and end-user experience.
- WiFi network monitoring: 802.11ax network assurance probes (WiFi 6E) ensure constant verification of WLAN enterprise grade connection (e.g. EAP-TLS), including signal strength, noise, and DHCP.
- Remote worker network monitoring: NetBeez offers lightweight software clients that collect key metrics to diagnose issues caused by slow internet speeds, unstable VPN connections, bad WiFi, and more.
Deploying NetBeez
Step 1: Deploy network agents in private and public networks
The Network Agents are hardware (Wi-Fi or Ethernet), virtual, or docker appliances. They are deployed in private and public networks to continuously monitor network availability and performance. Install one or more hardware or virtual appliances at each branch office, data center, and headquarters.
Step 2: Install remote worker agents for end-users
The Remote Workers Agents monitor and test a network availability and application performance from end-user perspective. These lightweight software clients are compatible with operating systems such as Windows, Mac OS, or iGel. They provide comprehensive performance data, including the status of the user’s wired and wireless network, internet speed, and endpoint performance. By analyzing data from both network agents and remote worker agents, IT teams gain a thorough understanding of digital experience.
Step 3: Configure network monitoring targets and scheduled tests
Once the agents show up on the NetBeez dashboard, you can start monitoring the network and applications. NetBeez offers two complementary methods for network and application monitoring: targets and scheduled tests.
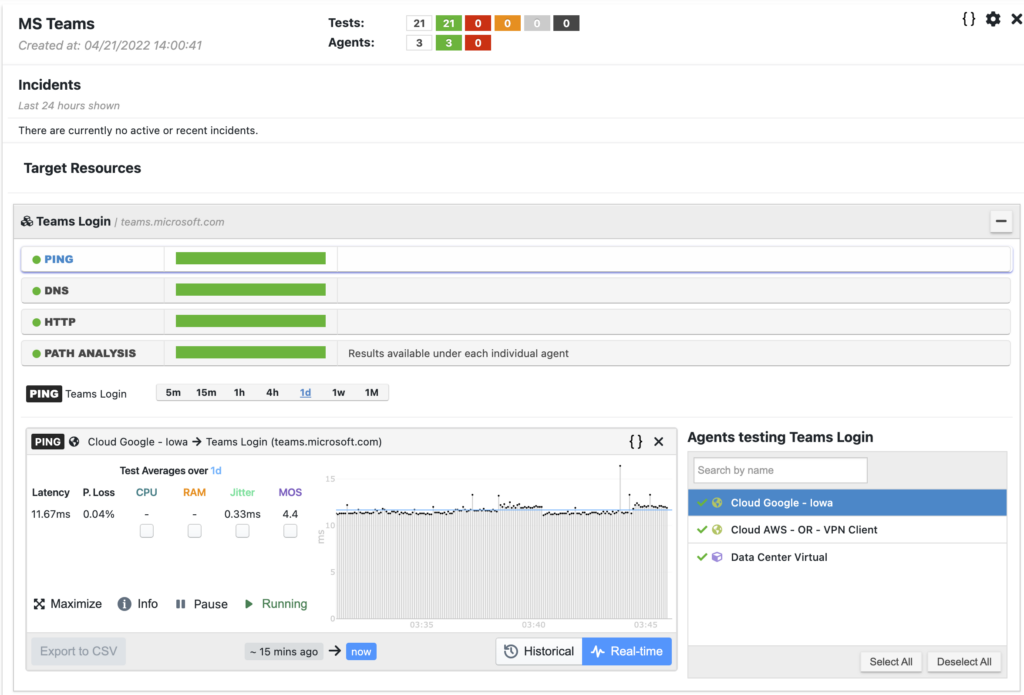
Targets are web or SaaS applications monitored via continuous network monitoring tests. These tests are ping, DNS, HTTP, traceroute and path analysis. They run at regular intervals, expressed in seconds. They provide real-time and historical performance data on internet connectivity, network topology, and more. Performance metrics such as latency, packet loss, DNS and HTTP response times are crucial for proactive detection of network problems. For example the following screenshot report a target to MS Teams.
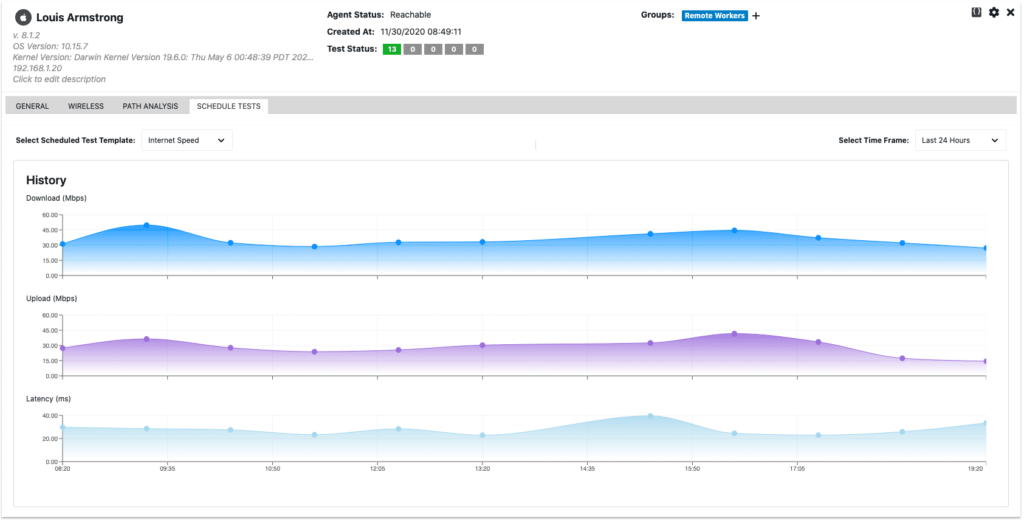
Scheduled tests like iperf, speed test, and VoIP, provide network performance metrics such as download and upload speed against internet servers and cloud locations. These tests run according to a user-defined schedule, such as hourly or daily based on needs. In the following screenshot a network speed test from an end-user laptop reports download speed, upload speed, and latency.
Conclusion on Remote Network Monitoring
Remote network monitoring is essential for managing distributed network infrastructures, allowing organizations to detect and respond to issues without being physically present. This monitoring system addresses challenges traditional tools cannot, offering real-time insights into network performance, including end-user experience, which is particularly valuable for organizations with multiple locations or remote workers. Tools like NetBeez provide comprehensive solutions for hybrid networks, WiFi assurance, and remote worker support. NetBeez delivers real time visibility and help reduce troubleshooting time and ensure optimal network performance. It becomes an indispensable tool for modern IT operations. If you want to learn more about NetBeez, request a product tour, or start a free trial.