Many IT professionals find themselves dedicating a significant amount of time each week or month to troubleshooting remote application issues, often discovering that users are already aware of these issues before they are. Implementing a robust network monitoring solution can proactively detect network and application problems, leading to a reduction in troubleshooting time and an enhancement of overall efficiency in resolving issues.
Network Complexity and Troubleshooting
The number of hardware and software components that are part of an enterprise network increase based on the number of locations and IT services that are supported. Something simple like a user accessing a company hosted browser-based application relies on the availability and performance of multiple systems.
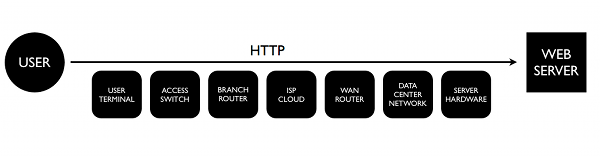
In most medium and large enterprises, each component is managed by a different team: routers, switches, and access points by the network team, the user terminal by the desktop team, the application, servers, and operating systems by other teams. Most of the times, each one of these teams has its own monitoring or vendor-based management tool and integrating them together is not always possible or successful.
So when a user reports a remote application issue, what team would the NOC operator call?
When you have an application performance issue, where do you start looking at, the network or the application layer?
Fault Isolation is Key When Troubleshooting Remote Application Issues
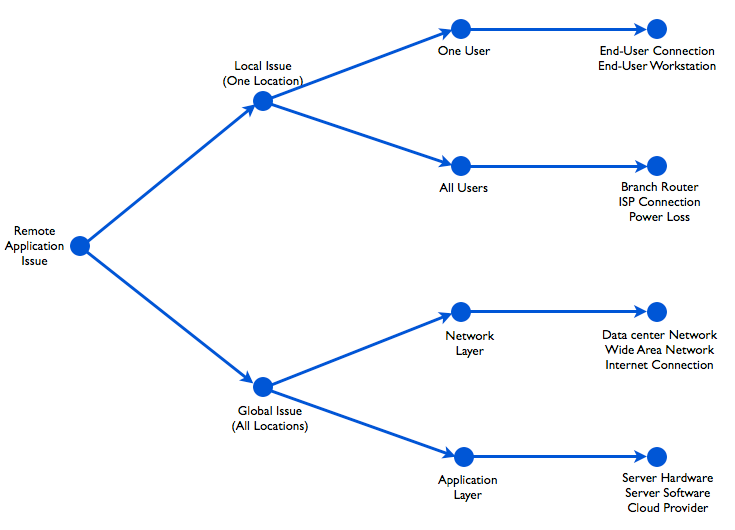
To determine the root cause of a remote application issue, there are two simple questions that you must answer:
- How many locations are affected? (Global versus Local)
- Is it on the network side or on the application side? (Network versus Application)
Answering these two questions enables your IT staff to quickly identify the scale of the problem, isolate the components within your IT infrastructure that are causing problems, and quickly escalate the ticket to the right group.
How NetBeez can help?
NetBeez provides information about local versus global and network versus application in a simple and intuitive way on its browser-based dashboard. By installing one hardware agent in every network location you will know if the issue is affecting one or more locations without waiting for calls from the end users.
Step 1 – Deploy network monitoring sensors
In this initial step, the network administrator installs the network monitoring agents. NetBeez provides two options based on the environment being monitored:
- Network agents are hardware, virtual or software appliances meant to run on-premises at remote branch offices, public clouds, and data centers. The data collected by these units will help network administrators understand what is the overall internet performance within the organization.
- Remote worker agents are software clients for Windows and Mac operating systems for end-user laptops or desktops. The data collected by these units are crucial to monitor the internet speed of work-from-home or remote employees. This method also removes any troubleshooting from the remote users, extending a network support team’s visibility beyond the corporate offices.
Step 2 – Create network monitoring targets and speed tests
NetBeez offers two complementary methods for troubleshooting remote application issues:
- Targets represent applications that are monitored via continuous tests such as ping, DNS, HTTP, traceroute and path analysis. These tests run at regular intervals, providing real-time and historical performance data on internet connectivity. Metrics such as latency, DNS resolution time, and HTTP performance are crucial for proactive detection of remote application issues.
- Scheduled tests such as network speed and iperf provide download and upload speed against internet servers and cloud locations. These tests run according to a user-defined schedule, such as hourly or daily based on needs.
Step 3 – Configure alerts and notifications methods
The last important step of the configuration is to enable notifications when NetBeez finds anomalies in the network. By default, NetBeez generates alerts either when a target detects a loss of connectivity with ping, or a service interruption with DNS and HTTP.
NetBeez also supports performance alerts by comparing a short-term moving average with a fixed value or to a long-term baseline. This simplifies SLA enforcements or smart detection of performance degradation. Notifications enable network administrators and support teams to get an email or some other events when an alert is triggered.
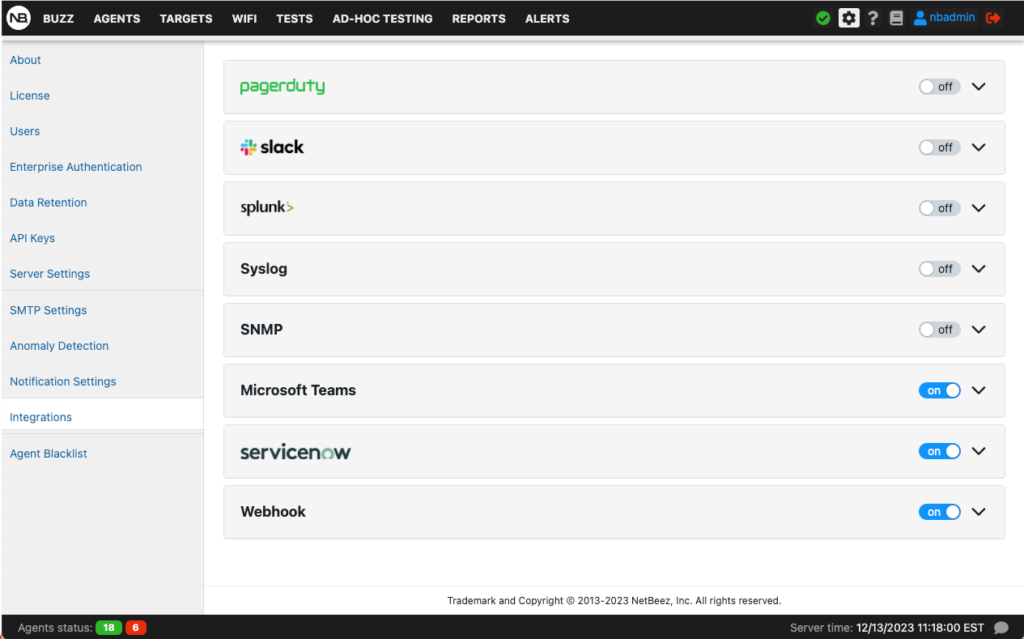
NetBeez can send notifications via standard protocols such as SMTP, SNMP, Syslog, and webhooks. It also supports out-of-the-box integrations with third-party systems such as ServiceNow, MS Teams, Slack, and PagerDuty.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting remote application issues in large and complex enterprise network environments is challenging. When working on a remote application issue, you cannot start looking into multiple network management tools that provide too much detailed information at the component level. It’s important to start with a 9,000 ft. view of the problem and then drill down into the details.
NetBeez offers a user-friendly browser-based dashboard that provides real-time and historical performance data, allowing network administrators to easily visualize network and application performance across multiple locations. With NetBeez, IT teams can proactively identify potential issues before they impact end-users, ultimately improving the overall user experience and minimizing downtime. By streamlining the troubleshooting process and providing actionable insights, NetBeez empowers organizations to maintain a high level of network reliability and performance in today’s increasingly complex IT environments. If you want to learn more about NetBeez, request a demo.