What’s the whois service?
Whois is an Internet service that lets you discover the registered users and their contact information associated with IP addresses, Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDN), or Autonomous Systems (AS). This service is used by network engineers and administrators when determining the identity of a remote host that is attempting to access a local server or network.
Another use case is to obtain the network names and autonomous system numbers associated with the intermediate hops of a traceroute test; this way, network troubleshooters can easily find the networks which your traffic is traversing. Perhaps these networks are causing high latency or packet loss.
History of the whois service
The whois service was first created in the 1970s by Elizabeth J. Feinler and her team, which was part of the Stanford Research Institute (SRI). Elizabeth’s team worked on many projects sponsored by the Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) that aimed at documenting and managing the resources available to ARPANET users and organizations, such as domains.
At the time, all the whois information was centrally managed on one server setup in the Stanford’s Network Information Center (NIC). The SRI office would also centrally manage new domain registrations, including whois information for ARPANET users. This process, which was also via phone during business hours, was sufficient in the early days of what is now known as the Internet.
However in the 1980s with the commercialization of the Internet it became clear that such processes were limiting the growth and expansion of the Internet and would require an update. After several discussions, it was decided that the management and registration of top-level domains and IANA functions would be assigned to the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN).
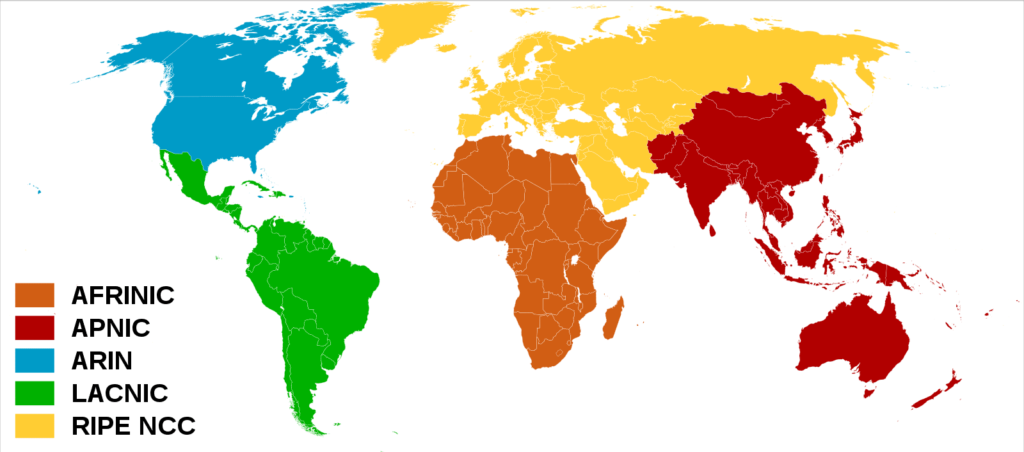
Today, whois functions are handled by regional Internet registries (RIR) which may cross reference whois entries. The below picture shows how whois entries are globally managed based on the physical location of the entity.
How to run whois
The service is available via a command-line utility whois installed by default on most Unix-like operating systems and Windows. On the command line, the user has to type the command whois followed by the parameter (IP, FQDN, or ASN).
For example, if I run whois netbeez.net I will display the following information (truncated for brevity):
% IANA WHOIS server % for more information on IANA, visit http://www.iana.org % This query returned 1 object refer: whois.verisign-grs.com domain: NET organisation: VeriSign Global Registry Services address: 12061 Bluemont Way address: Reston Virginia 20190 address: United States ... # whois.godaddy.com Domain Name: NETBEEZ.NET Registry Domain ID: 1752901950_DOMAIN_NET-VRSN Registrar WHOIS Server: whois.godaddy.com Registrar URL: http://www.godaddy.com Updated Date: 2020-10-18T09:29:08Z Creation Date: 2012-10-17T17:01:16Z Registrar Registration Expiration Date: 2022-10-17T17:01:16Z Registrar: GoDaddy.com, LLC Registrar IANA ID: 146 ... Registry Registrant ID: Not Available From Registry Registrant Name: Registration Private Registrant Organization: Domains By Proxy, LLC Registrant Street: DomainsByProxy.com Registrant Street: 14455 N. Hayden Road Registrant City: Scottsdale Registrant State/Province: Arizona Registrant Postal Code: 85260 Registrant Country: US Registrant Phone: +1.4806242599 Registrant Phone Ext: ... URL of the ICANN WHOIS Data Problem Reporting System: http://wdprs.internic.net/ >>> Last update of WHOIS database: 2021-06-22T11:27:34Z <<<
Many whois domain results, like the one above, are masked by a proxy organization for privacy purposes, to shield contact information including emails from spammers. If that’s the case, competent authorities will have to contact the proxy organization should there be a legal claim or investigation.
Conclusion
Whois is a “must have” utility in a network engineer’s tool bag. This Internet service is like the Yellow Pages – users can look up who owns or manages a specific Internet property, whether that is a website, an IP address space, or an entire autonomous system.